Metallurgical Furnace
Produktbeskrivelse
Metallurgical Furnace
CIC main advantage in nonferrous metallurgical furnace lies in the manufacture of horizontal rotary furnace, Rotary refining furnace and bottom blown furnace. Rotary furnace is the main metallurgy furnace equipment used to treat copper and nickel sulfide in nonferrous metallurgical production. The rotary furnace does not need fuel, and only relies on the heat released by the oxidation reaction of iron and sulfur in copper and sulfur with the air blown into the heavy equipment machinery solution to provide all the heat expenditure.
Metallurgical Furnace News
Metallurgical furnaces operation process
Instruction of Metallurgical Furnace
Rotary refining furnace is mainly used for refining liquid crude copper and copper mining process. The refining operation generally includes four stages: feeding, oxidation, reduction and casting. The product is to provide a qualified anode plate for copper electrolytic refining. Therefore, rotary refining furnace is also called a rotary anode furnace.
The main characteristics of rotary refining furnace are simple structure, large furnace capacity, high degree of mechanical automation, strong controllability, good sealing and low energy consumption. Rotary refining furnace is mostly used in pyrometallurgical refining of large or extra large copper smelters.
Structure of Metallurgical Furnace
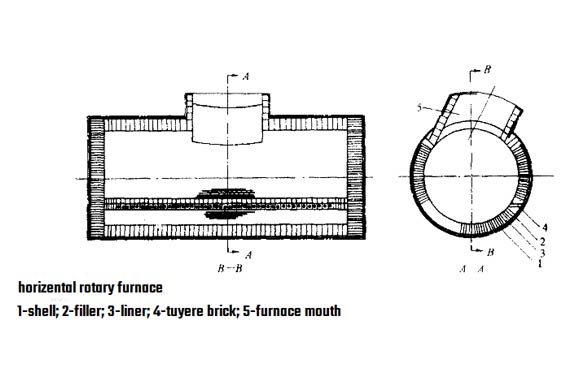
The horizontal rotary furnace is a kind of smelting equipment for blowing matte or nickel into coarse copper or high matte in the smelting process of non-ferrous metals such as copper and nickel. Its specification is expressed by the output of each furnace. The furnace body is cylindrical (see Fig. 1), and a furnace mouth is set in the middle for charging, smoke exhaust, slag discharge and discharging. A row of tuyeres is set at the furnace side along the horizontal direction to blow in the air. The lining of the horizontal converter is made of magnesia or chrome magnesia refractory.
Figure Of Horizontal Rotary Furnace
Rotary refining furnace is mainly composed of furnace body, supporting device, drive and control system. The main supporting equipment includes combustion device, combustion air system, oxidant, reductant, steam, compressed air, cooling water and process piping (as shown in Figure 2 below).
The cylindrical furnace body is provided with a furnace mouth for charging and discharging copper. The furnace mouth is equipped with a furnace cover. The furnace cover is only opened when charging and discharging copper. The melting period, oxidation period and reduction period are all covered. A small amount of tuyere is set on the side of the furnace body, high-pressure air is introduced in the oxidation period, and the reducing agent is introduced in the reduction period. When the tuyere is not in operation, it is placed above the melt surface. When the redox operation is carried out, the furnace is tilted to make the tuyere embedded in the melt. The rotary refining furnace needs an external heat supply, so it is equipped with a fuel combustion device and exhaust port.
Figure About Rotary Refining Furnace
Related Issues of Metallurgical Furnace
What are the masonry methods of the horizontal rotary furnaces?
There are two kinds of masonry methods: rotary furnace body construction method and arch tire construction method. The construction procedure is to build the end wall first, then the circular liner, and finally the furnace mouth. Before the liner of the furnace is built, the driving device of the furnace body must pass the trial operation and be locked; The gap between the end cover of the furnace shell and furnace body should be plugged with asbestos rope. The circular liner and end wall shall be dry laid with staggered joints, and the brick joint shall not be greater than 1.5 mm. The staggered joints between tuyere and furnace mouth shall be wet-laid, and the brick joint shall be no more than 2 mm.

